

Pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destinationĬhain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes)Ĭhain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 33 packets, 5915 bytes) # iptables -L -vnĬhain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 39 packets, 4642 bytes) In this case we don’t have to do any settings in iptables. My iptables on VPS has the default configuration, so is not dropping any packets. I’ve opened port 3333 in the Firewall on the management web-interface of the VPS.
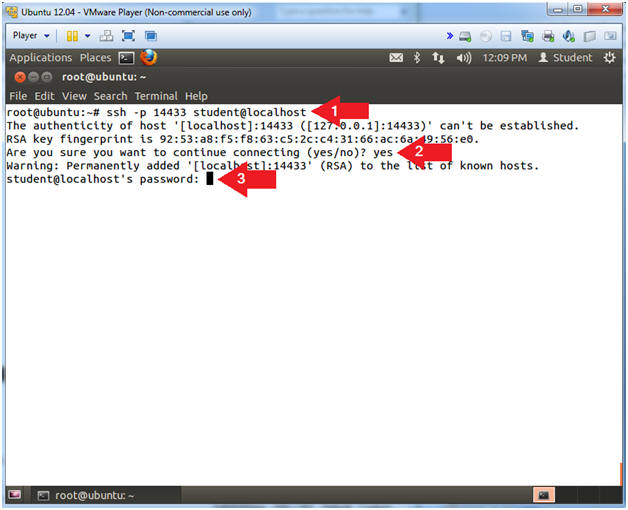
How can you achieve this, I’ll explain you in the following lines. Reverse SSH tunneling allows you to create a connection from the remote computer to a local computer and using this established connection to set up a new connection from your computer back to the remote computer. This computer could be placed behind a firewall or a router (NAT) whose rules or settings cannot be changed.Īn easy and practical solution that could help us in this case is to set up a reverse SSH tunnel on Linux. I am sure that the server accepts remote connections, because I have connected to it remotely while logged in via RDP to a different machine within the remote network.There are cases when a remote computer could be hard to reach. Instance name is correct and that SQL Server is configured to allow remote

The server was not found or was not accessible. I can then actually test the connection by telnetting to localhost 3398, and I get a connection: the screen clears and I can type characters to some listening process.īut when I try to connect SSMS to localhost:3398, it times out and then claims that there is no SQL Server listening on that port: Cannot connect to localhost:3398Ī network-related or instance-specific error occurred while establishing a connection I've set up a local port (3398) to redirect to the SQL Server port on the remote instance (元398 -> :1433). I would very much like to be able to locally access SQL Server instances running on these servers in the same way. We access the machines on that network by first opening an SSH connection to a gateway server, and then SSH-tunneling RDP over a local port.
#Setting up reverse ssh tunnel linux code#
In my development shop, we deploy code on virtual servers that sit on a remote network.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
